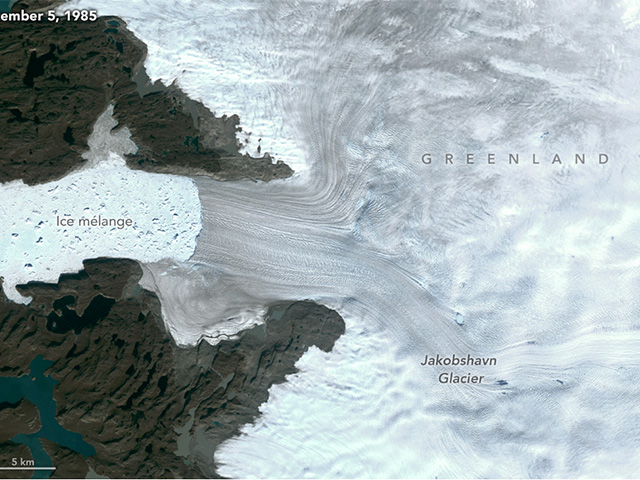
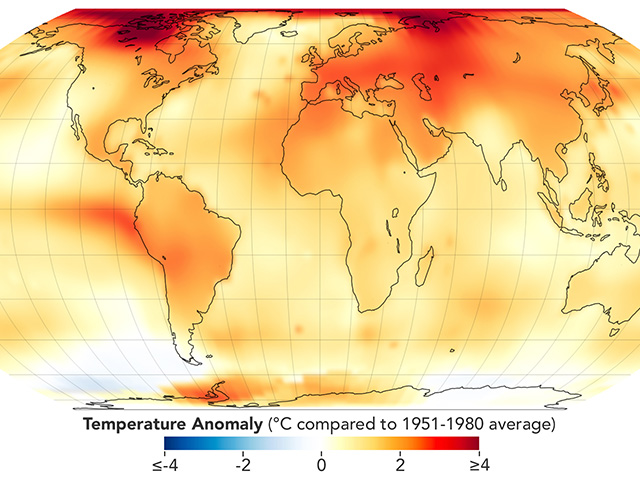
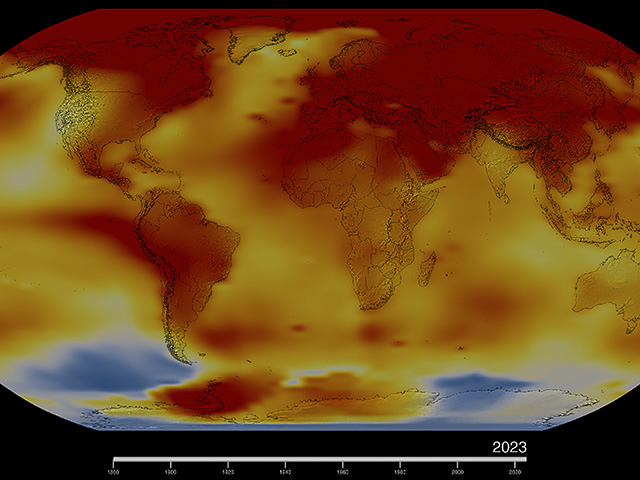
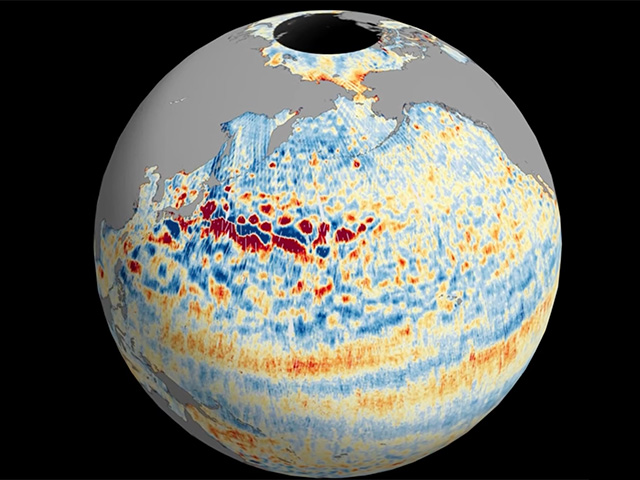
Atmosphere
The atmosphere is a mixture of nitrogen (78%), oxygen (21%), and other gases (1%) that surround Earth. Most of our weather and clouds are found here - the atomosphere is an important part of what makes Earth livable.
BiosphereThe biosphere is all life on our planet including life on land and in the oceans. The biosphere influences the amounts of some of the major greenhouse gases such as methane, carbon dioxide, and nitrous oxide - so it is an integral part of global climate.
FeedbacksClimate feedbacks are interactions between processes within the climate system that result in an initial process triggering changes in a second process that in turn influence the initial one.
ForcingsClimate forcings refer to an energy imbalance caused by natural or man-made processes causing an energy imbalance between incoming energy from the Sun and outgoing heat from the Earth.
Global climate changeGlobal climate change is change recorded over an extended length of time (decades or longer) with regards to precipitation, temperature or wind caused by natural and/or manmade factors.
Global warmingGlobal warming refers to the increase in the average temperature of the earth's atmosphere, sufficient to cause climate change.
HydrosphereThe hydrosphere is the water layer of the Earth. About 70% of the Earth's surface is covered with water, most of which is in the oceans. Only a small portion of the Earth's water is freshwater, found in rivers, lakes, and groundwater.
LithosphereThe lithosphere is made up of the Earth's crust and the upper part of the mantle layer underneath. The lithosphere extends about 80 km deep and is broken into giant plates that move and shift, causing earthquakes.