DIRECT MEASUREMENTS: 1958-PRESENT
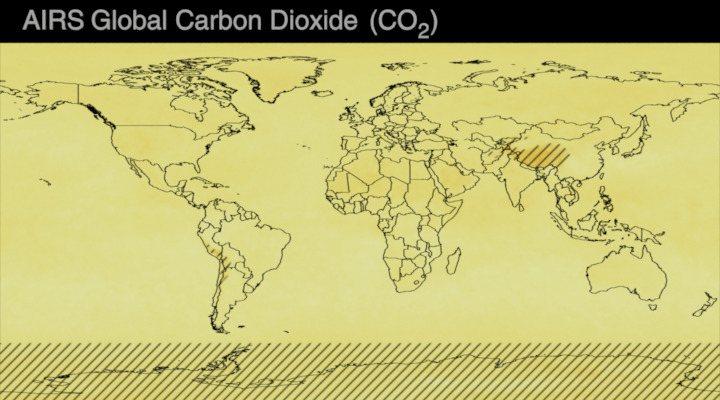
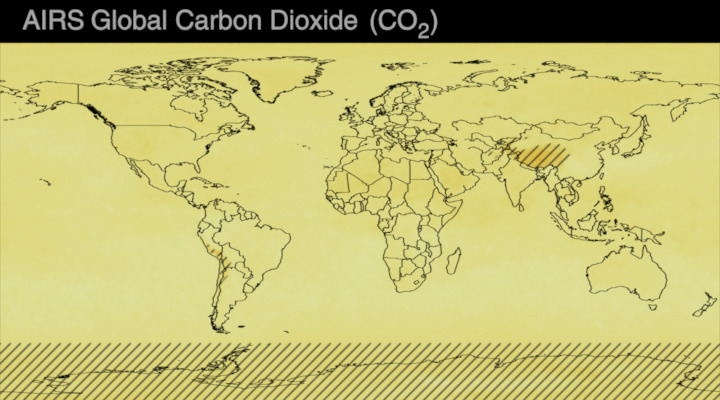
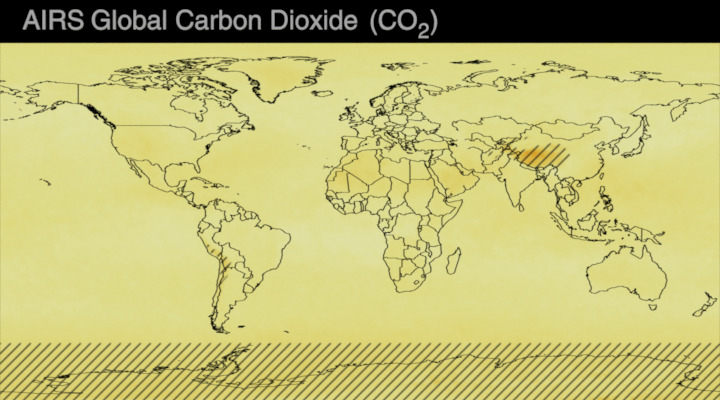
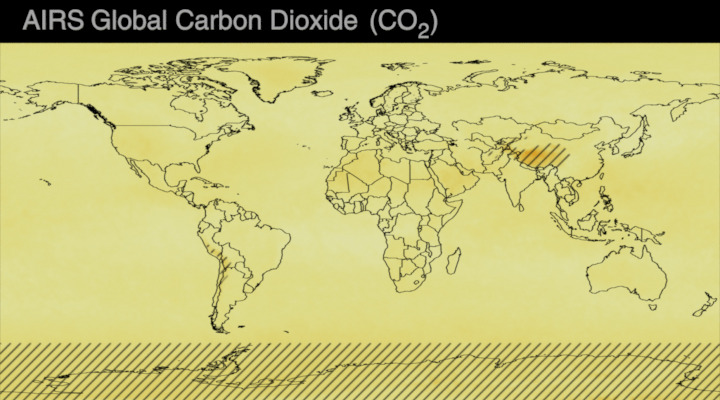
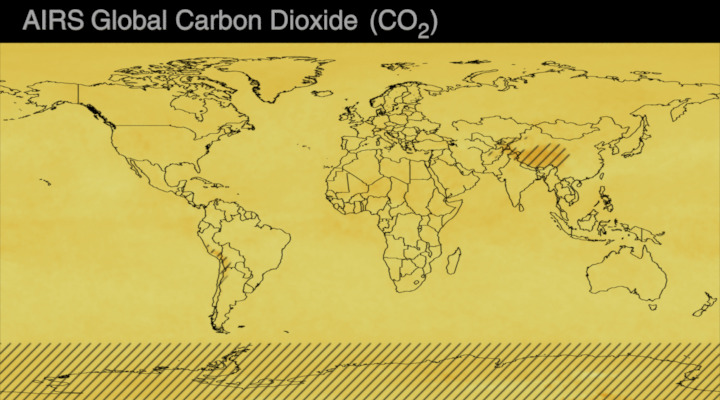
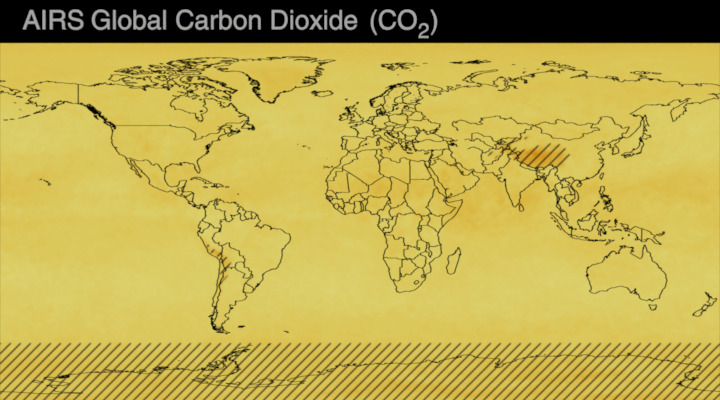
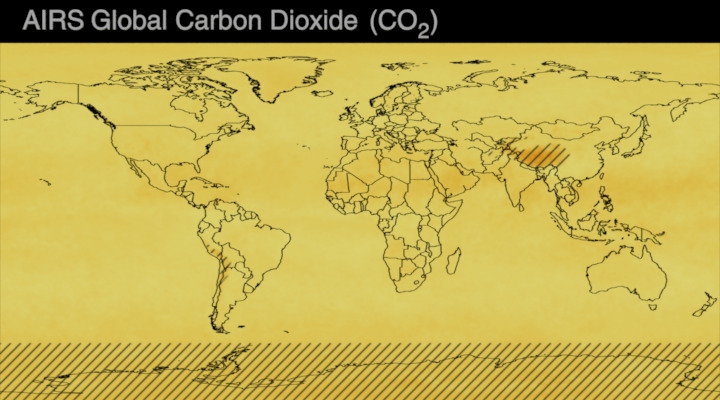
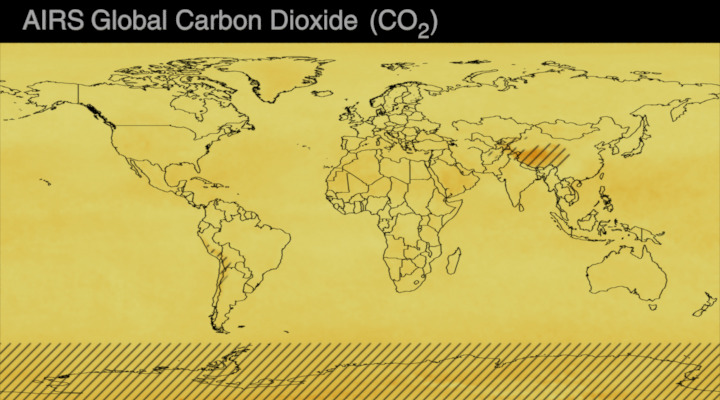
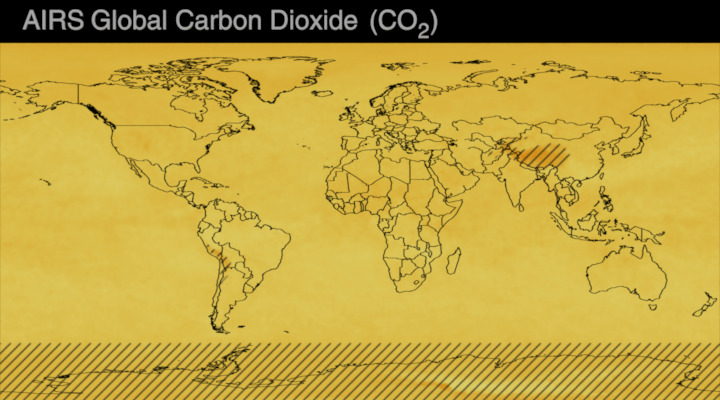
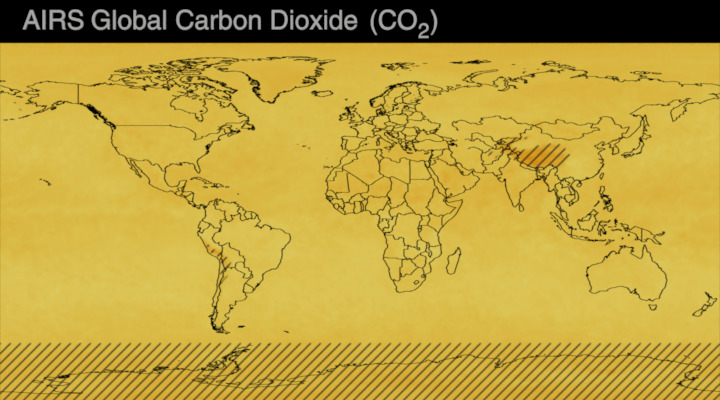
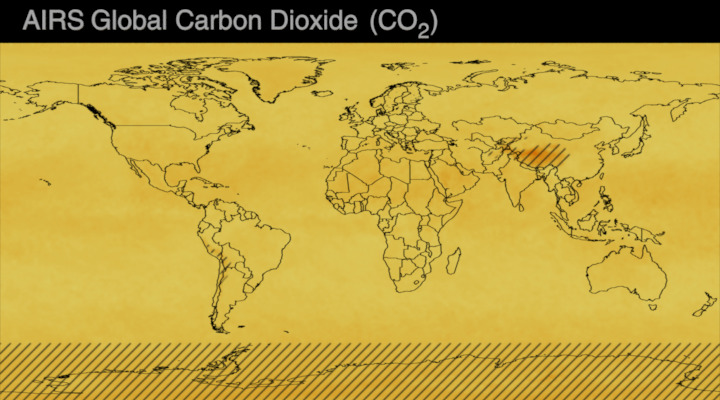
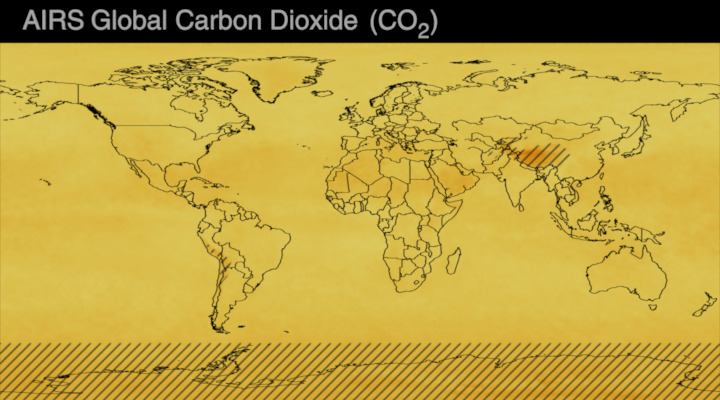
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is an important heat-trapping gas, or greenhouse gas, that comes from the extraction and burning of fossil fuels (such as coal, oil, and natural gas), from wildfires, and from natural processes like volcanic eruptions. The first graph shows atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2) levels measured by NOAA at Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii, since 1958.
Since the onset of industrial times in the 18th century, human activities have raised atmospheric CO2 by 50% – meaning the amount of CO2 is now 150% of its value in 1750. This human-induced rise is greater than the natural increase observed at the end of the last ice age 20,000 years ago.