1. Visible Earth
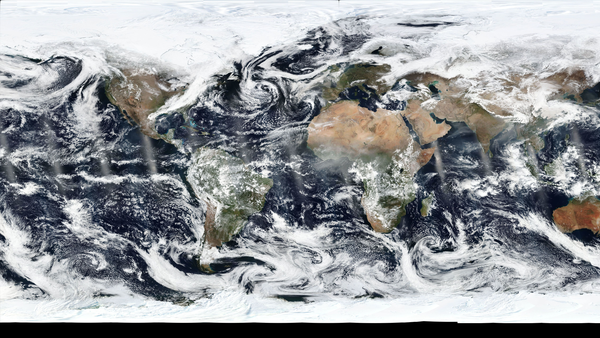
What satellite's real color images are used to create a daily mosaic selfie of Earth?

Use Earth Now to explore our planet’s vital signs. This quiz-based treasure hunt will have you delving into data layers and researching satellite missions as you seek the correct answers and learn more about planet Earth along the way.

What satellite's real color images are used to create a daily mosaic selfie of Earth?

How many satellites are visible orbiting Earth in Satellites Now?

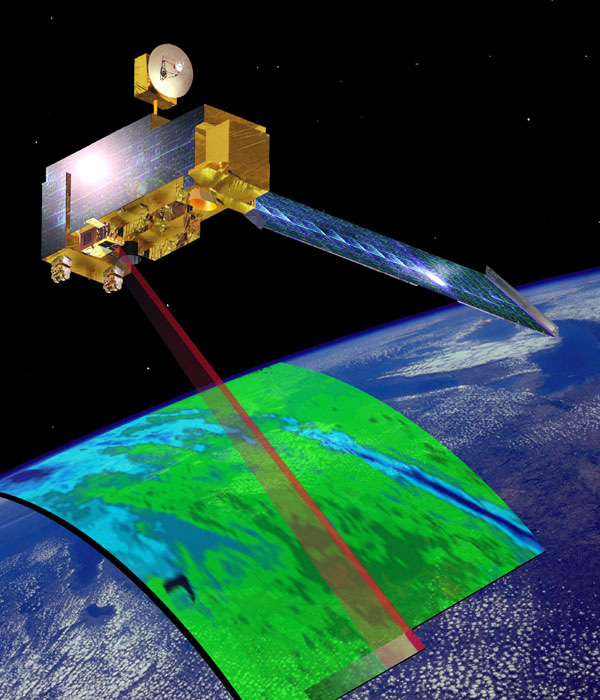
Using the Missions menu, what satellite classified as studying the land has been in orbit the longest?


How many orbits per day around Earth does the International Space Station (ISS) make?

Which mission uses gravity to study the movement of water and ice?

Using the More menu, what city name shown in the Earth Now application is closest to the South Pole?

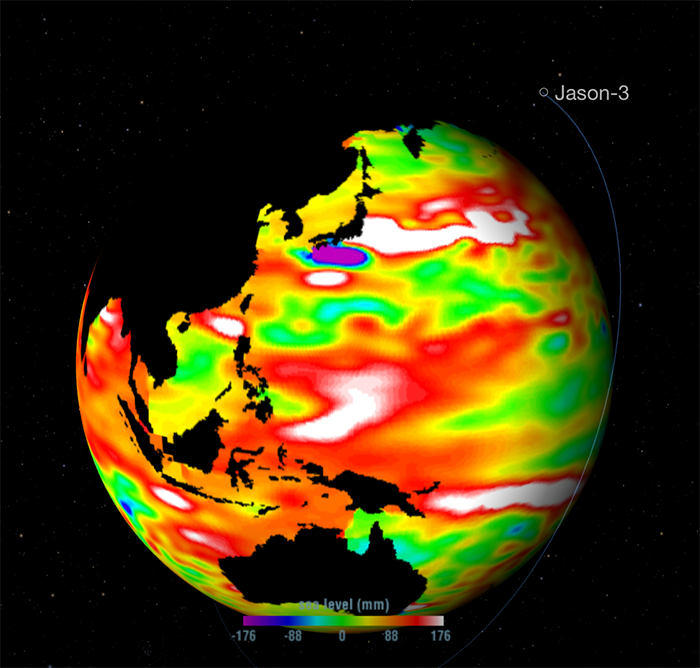
When visualizing sea level, what colors equate to higher sea level variation?


Carbon dioxide, or CO2, is a greenhouse gas derived from human and natural activities. What is the name of the mission launched in 2014 to measure this gas contributing to climate change?
